
Schematic of leadacid batteries. Reproduced with permission [35].... Download Scientific Diagram
- Definition, Diagram & Working. In this topic, you study the definition, diagram and working of the lead acid battery and also the chemical reactions during charging and discharging. The combination of two or more than two cells suitably connected together is known as a battery. In case of lead acid cell, the cell has got the following parts.

How a lead acid cell works. Electrical Academia
Context 1. number as such also depends on the dynamics of changes in the load of the analysed battery. The electric diagram of the discussed n-order model of a single cell of the.

Geometry of a leadacid cell. (a) macroscopic shape and dimensions; (b)... Download Scientific
Plante Process In this process two sheets of lead are taken and immersed in dilute H 2 SO 4. When an current is passed into this lead acid cell from an external supply, then due to electrolysis, hydrogen and oxygen are evolved.

Lead acid battery, Construction and, Working, and Charging
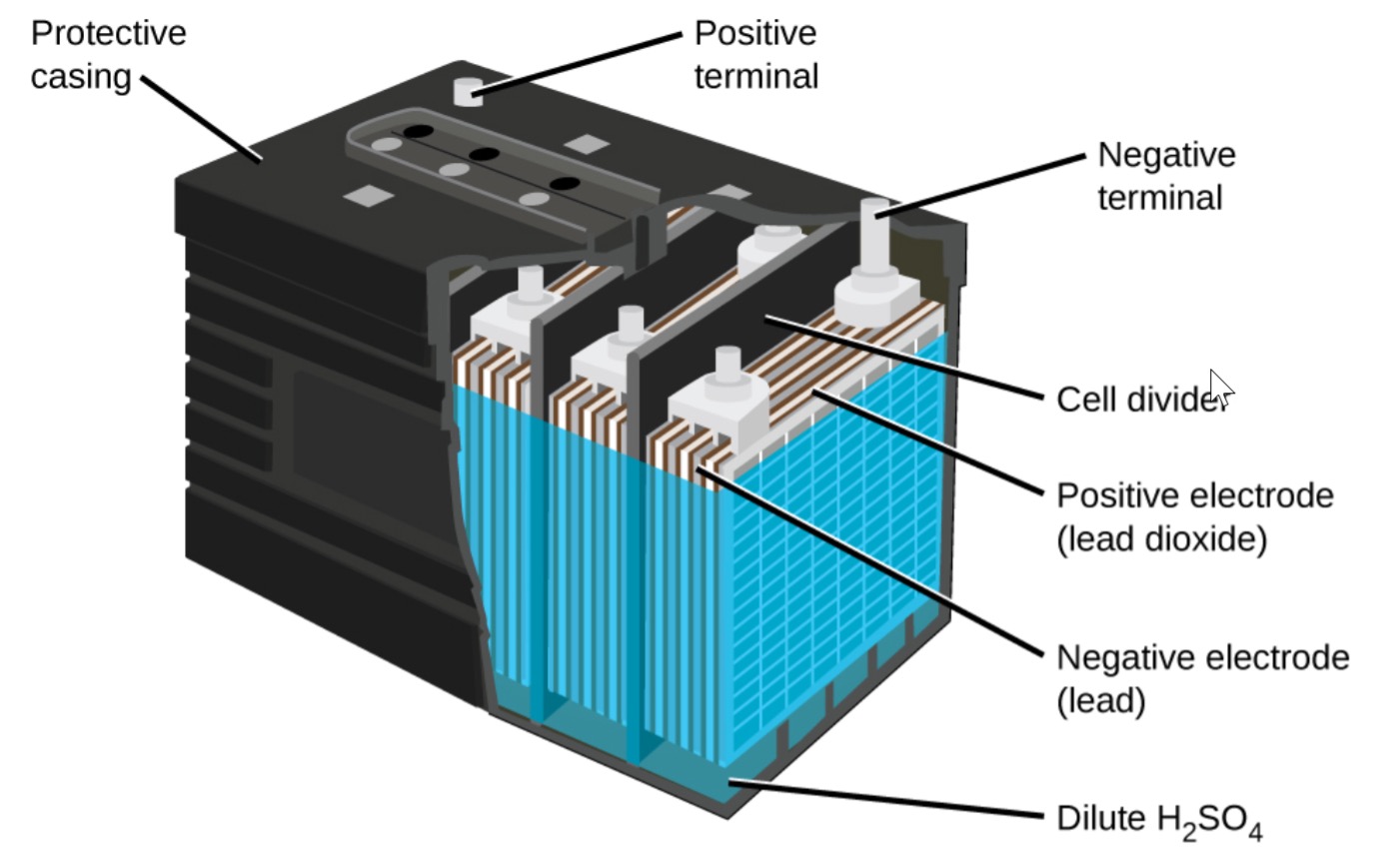
A lead acid battery consists of a negative electrode made of spongy or porous lead. The lead is porous to facilitate the formation and dissolution of lead. The positive electrode consists of lead oxide. Both electrodes are immersed in a electrolytic solution of sulfuric acid and water.

Schematic diagram of a leadacid battery. Download Scientific Diagram
The open circuit voltage of this battery is. VO = (2:041. 0:12pH) V: (22) To see the range of conditions in which this battery can e ectively operate, we consider the Nernst equation for various possible reactions: Lecture 9: Fuel cells and lead-acid batteries 10.626 (2011) Bazant. Lead / sulfuric acid (half-cell) reactions:

a Characteristics curve of one lead acid cell at different discharge... Download Scientific
Positive: PbO 2 (s) + HSO 4- (aq) + 3H 3 O + (aq) + 2e - -> PbSO 4 (s) + 5H 2 O (l) (reduction) Lead Acid Battery Discharging Lead sulfate is formed at both electrodes. Two electrons are also transferred in the complete reaction. The lead-acid battery is packed in a thick rubber or plastic case to prevent leakage of the corrosive sulphuric acid.

Engineering Photos,Videos and Articels (Engineering Search Engine) CHAPTER 2 PRIMARY AND
Lead-acid batteries are one of the most common secondary batteries, used primarily for storing large cell potential. These are commonly found in automobile engines. Its advantages include low cost, high voltage and large storage of cell potential; and disadvantages include heavy mass, incompetence under low-temperatures, and inability to.

Basics of VRLA Type of Batteries
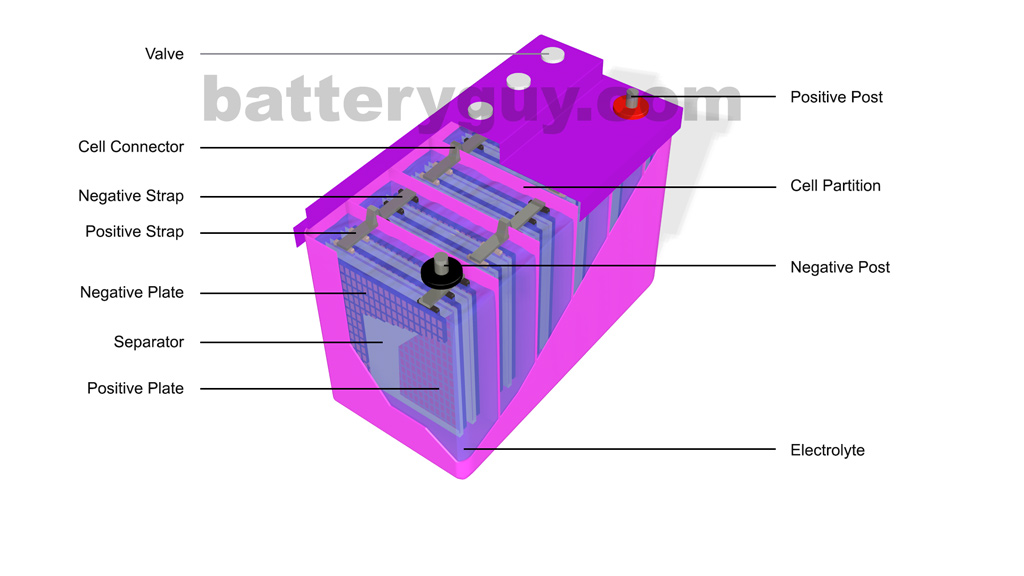
This corresponds that lead acid cells possess a high amount of power to weight proportions.. The lead acid battery diagram is. Lead Acid Battery Diagram Container. This container part is constructed with ebonite, lead-coated wood, glass, hard rubber made of the bituminous element, ceramic materials, or forged plastic which are placed on the.
What You Need to Know About LeadAcid Batteries BoatTEST
The lead-acid battery is a type of rechargeable battery first invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté. It is the first type of rechargeable battery ever created. Compared to modern rechargeable batteries, lead-acid batteries have relatively low energy density. Despite this, they are able to supply high surge currents.
What is a lead acid battery? Knowledge Base
Context 1. serve primarily to isolate the plates and to prevent short circuits between the plates. During the chemical reaction, the voltage between the lead plates and the lead dioxide.

Primary cell electronics Britannica
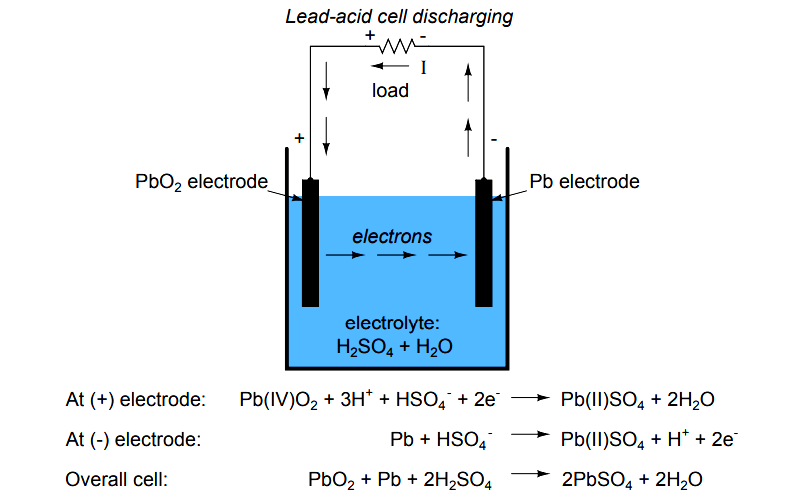
The lead acid battery uses lead as the anode and lead dioxide as the cathode, with an acid electrolyte. The following half-cell reactions take place inside the cell during discharge: At the anode: Pb + HSO4- → PbSO4 + H+ + 2e-. At the cathode: PbO2 + 3H+ + HSO4- + 2e- → PbSO4 + 2H2O. Overall: Pb + PbO2 +2H2SO4 → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O.

Lead Acid Battery Construction, Working, Charging Electrical Academia
difference (usually measured in volts) is commonly referred to as the voltage of the cell or battery. A single lead-acid cell can develop a maximum potential difference of about 2 V under load. A completely discharged lead-acid cell has a potential difference of about 1.75 V, depending on the rate of discharge. Capacity and Battery Ratings

How lead acid battery works Working principle animation YouTube
The lead-acid battery is the most commonly used type of storage battery and is well-known for its application in automobiles. The battery is made up of several cells, each of which consists of lead plates immersed in an electrolyte of dilute sulfuric acid. The voltage per cell is typically 2 V to 2.2 V.

All about Batteries Electrical A2Z
Lead-Acid Battery. The reaction of lead and lead oxide with the sulfuric acid electrolyte produces a voltage. The supplying of energy to and external resistance discharges the battery. Lead-acid batteries. Index. DC Circuits. Batteries. HyperPhysics ***** Electricity and Magnetism. Go Back.

PPT The Lead Acid Electric Battery PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1810673
The most common type of heavy duty rechargeable cell is the familiar lead-acid accumulator ('car battery') found in most combustion-engined vehicles. This experiment can be used as a class practical or demonstration. Students learn how to construct a simple lead-acid cell consisting of strips of lead and an electrolyte of dilute sulfuric acid.
Electron Activity in Chemical Reactions Lead acid Cell Battery
A lead-acid battery cell consists of a positive electrode made of lead dioxide (PbO 2) and a negative electrode made of porous metallic lead (Pb), both of which are immersed in a sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4) water solution. This solution forms an electrolyte with free (H+ and SO42-) ions. Chemical reactions take place at the electrodes: